Unit-1
HTML Tags
Lists
- Ordered List
- Unordered List
- Definition List
<h1>Ordered List</h1>
<ol>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Banana</li>
</ol>
<h1>Unordered List</h1>
<ul>
<li>Rose</li>
<li>Lilly</li>
</ul>
<h1>Unordered List</h1>
<dl>
<dt>Car</dt><dd>Which goes on road</dd>
<dt>Aircraft</dt><dd>Which goes in the air</dd>
</dl>Tables
Rowspan: Merging two rows
colspan: Merging two columns
<table>
<tr>
<th>Flower</th>
<th>Color</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Rose</td>
<td>Red</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Lilly</td>
<td>White</td>
</tr>
</table>Images
Attributes:
- src: Source file
- alt: Image name
<img src="rose.jpg" alt="Rose">Forms
Attributes:
- action: script to run
- method: GET or POST
- target: Where the result is displayed
Controls:
- Text
- Password
- Checkboxes
- Radio
- Selectboxes
- Submit and Reset buttons
<form action="example.com" method="POST">
First Name:<br>
<input type="text" name="first"><br>
Last Name:<br>
<input type="text" name="last"><br>
Password:<br>
<input type="password" name="pass"><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit">Frames
We can divide the page into multiple section either column wise or row wise. Makes the webpage more intuitive.
<frameset rows="25%, 25%, *">
<framesrc="one.html">
<framesrc="two.html">
<framesrc="three.html">
</frameset>CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
Used to describe how the HTML elements are displayed. It is used to decorate a web page and make it more attractive.
Types:
- Inline
- Internal
- External
Inline: Styling in the same line
<body border=1px bgcolor="blue" color="yellow">
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
</body>Internal: Defining styles in HTML itself
<head>
<style>
body {
color: yellow;
background: blue;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
<head>External: Linking external styles to the HTML
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>Border, Padding and Margin
Border: Border around a HTML element
Padding: Space between text inside element and border of the element
Margin: Space outside the margin to other HTML elements
JavaScript
It’s a scripting language, we use it to make web pages more interactive and run scripts on the client side. Features:
- Light weighted
- Interpreted Based
- Event handling
- Validating User’s input
- Object-Oriented
- Client Side
- In-build functions
Declaring Variables
var: It’s used when we want to redeclare the same variable
let: It’s used when we want to redeclare the same variable but inside a block
const: When variable are constant throughout script we use const
Scope of variables
var is function-scoped, meaning it’s scope is inside a function.
let and const are block-scoped, meaning it’s scope resides inside a block like if block.
Event Handlers
| Attribute | Event |
|---|---|
| onclick | mouse click on object |
| ondbclick | on double click |
| onmouseover | cursor on the object |
| onmousedown | mouse button pressed |
| onmouseup | mouse button released |
| onmousemove | mouse is moved |
| onkeydown | a key is pressed |
| onkeypress | key is pressed or held down |
| onkeyup | key is released |
Example:
<html>
<head>
<script language="JavaScript">
function add() {
a = 10
b = 20
c = a + b
document.write("Addition is: "+c)
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="add()">
</body>
</html> Document Object Model (DOM)
The DOM is a top-down representation of all the elements that make up a web page. It’s the interface through which scripts interact with the web page. The Document Object Model represents the page as a tree structure, with the document as the root object, and each element, attribute, and piece of text as a node. This allows scripts to access and manipulate the content, structure, and style of the web page DOM is an interface for HTML. It defines the logical structure of document and the way document is accessed and manipulated. When an HTML document is loaded into a window, it becomes a document object.
Form Validation
<html>
<head>
<title>Form Validation>
<script>
function validate() {
var x = document.forms["myForm"]["name"].value;
if (x == "") {
alert("Name must be filled");
}
}
</script>
<head>
<body>
<form name="myForm" onsubmit="validate()">
Name:<br>
<input type="text"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>Unit-2
XML
XML stands for extensible mark up language. XML was created to structure, store and transport information. We can create our own tags in XML, its platform independent. It is case sensitive and all elements must have closing tags.
Well formed XML Document:
- Must have a root element
- All elements must have closing tags
- Tags are case sensitive
- Elements must be properly nested
Example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<person>
<name>John</name>
<age>19</age>
<height>186</height>
</person>DTD (Document Type Definition)
It’s purpose is to define structure of an XML document. It defines the structure with the list of defined elements. Using DTD we can specify various element types, attributes and their relationship. Basically DTD is used to specify the set of rules for structuring data in XML files.
Syntax:
<!ELEMENT element-name (element-content)>CDATA: It stands for character data. It will not be parsed and text inside will not be treated as markup language PCDATA: It stands for parsed character data. Data inside will be parsed and treated as markup language.
Example: .dtd file
<!DOCTYPE person
[
<!Element person (name, age, height)>
<!Element name (#CDATA)>
<!Element age (#PCDATA)>
<!Element height (#PCDATA)>
]>Types:
- Internal DTD
- External DTD
Internal DTD
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes" ?>
<!DOCTYPE person [
<!Element person (name, age, height)>
<!Element name (#CDATA)>
<!Element age (#PCDATA)>
<!Element height (#PCDATA)>
]>
<person>
<name>John</name>
<age>19</age>
<height>186</height>
</person>External DTD
XML file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<!DOCTYPE person SYSTEM "person.dtd">
<person>
<name>John</name>
<age>19</age>
<height>186</height>
</person>person.dtd File
<!Element person (name, age, height)>
<!Element name (#CDATA)>
<!Element age (#PCDATA)>
<!Element height (#PCDATA)>XML Schema
It is commonly known as XML Schema Definition (XSD). It’s used to describe and validate the structure and content of XML data. XML schema defines elements, attributes and data types. Schema element supports namespaces.
It also defines fixed and default values of elements and attributes and also allows the use of datatypes.
Syntax:
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">Data Types
- String
- Date
- Numeric
- Boolean
Example .xsd file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="age" type="xs:int"/>
<xs:element name="dob" type="xs:date"/>
<xs:element name="male" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:schema>Definition Types
- Simple: Its used only in the context of text
- Complex: This allow you to specify which child element your element can contain and provides structure to XML
- Global: You can define a single type which can used by all other references
Unti-3
CGI vs Servlet
| Basis | Servlet | CGI |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | It is thread based, for every new request new thread is created | It is process based, for every new request new process is created |
| Languages used | Written in Java | Written in any language |
| Object-Oreinted | It’s object oriented as it’s in java | Not always object-oriented as written in many languages |
| Portability | It is portable | Not portable |
| Persistance | Remains in memory until explicitly destroyed | Removed from memory after process is completed |
| Server Independence | It can use any of the web-server | Limited support |
| Data Sharing | Possible | Not possible |
| Link | Links directly to the server | Does not link the web-server directly to the server |
| Http Server | It can read and set HTTP server | It can neither read nor set HTTP server |
| Cost | Construction and destruction of threads is not costly | Construction and destruction of new processes is costly |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Platform dependency | It can be platform independent | Platform dependent |
Life Cycle of a Servlet
It contains four stages:
- Loading a Servlet
- Initializing a Servlet
- Request Handling
- Destroying a Servlet
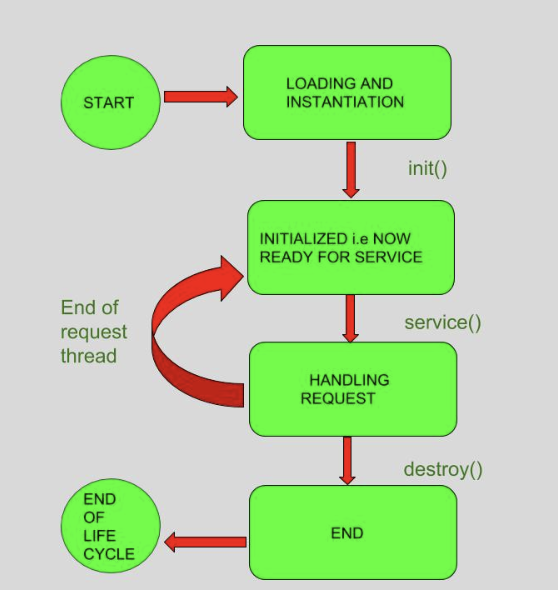
Life cycle methods:
- Init()
- service()
- destroy()
Deploying Servlet
- Download and Install the Java Software Developmentkit
- Download a server (Tomcat)
- Configure the server
- Setup deployment environment
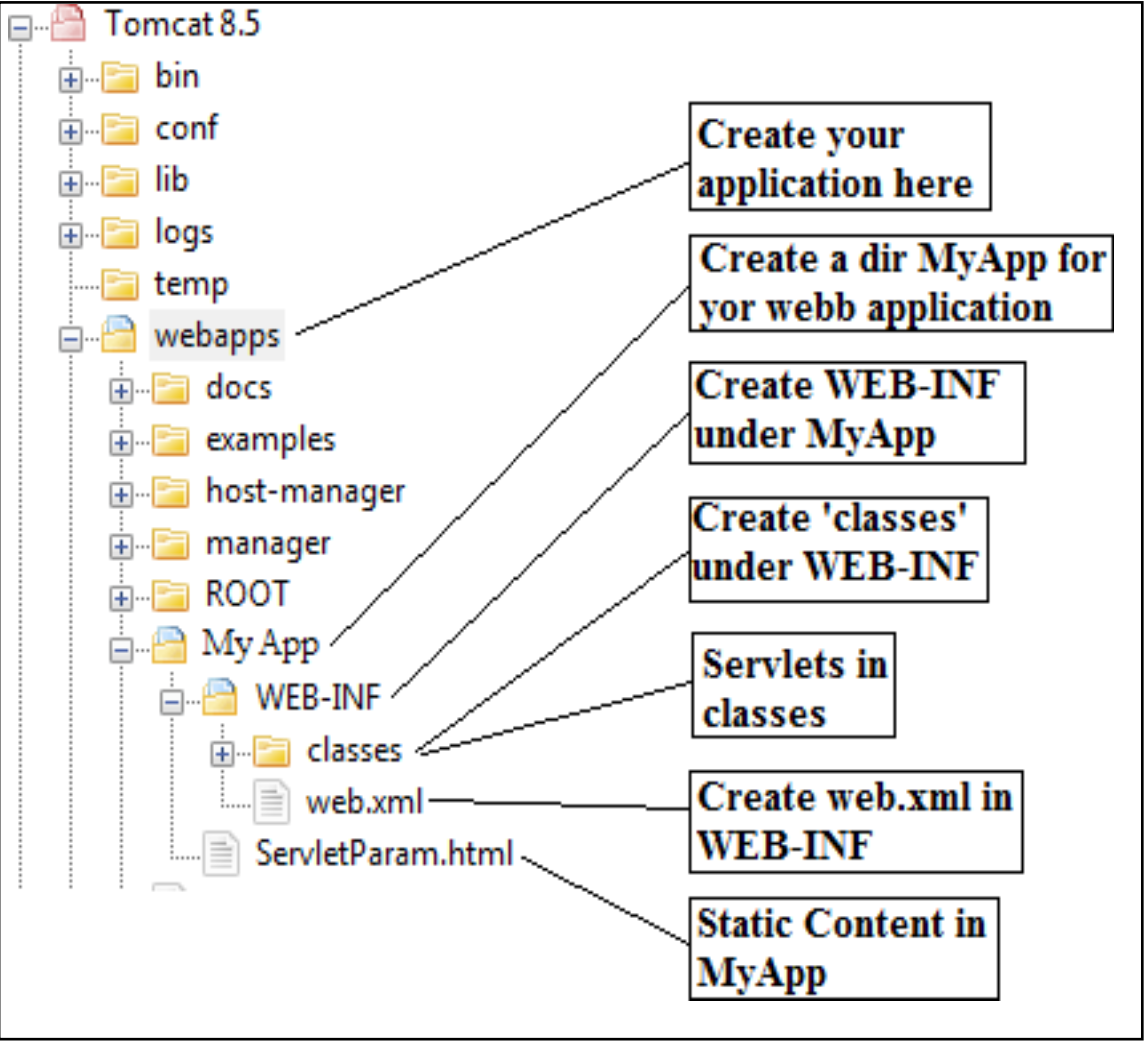
- Creating DemoServlet
- Compile Servlet and save the class files in classes folder
- Create a Deployment Descriptor (XML)
- Start Tomcat Server
- Open browser and type http://localhost/MyApp/DemoServlet
Session Tracking
Session simply means a particular interval of time. Session tracking is a way to maintain state of a user. HTTP protocol is stateless, each request is considered as a new request, so we need to maintain the states using session tracking techniques.
Session Tracking Techniques:
- Cookies
- Hidden FormField
- URLRewriting
- HttpSession
Cookies
Cookies are text files stored on the client computer and they are kept to maintain various information tracking purpose
It involves three steps:
- Server script send a set of cookies to the browser in response header
- Browser stores this information on the machine
- For future request the browser send those cookies to the server and server uses the information to identify user
Creating Cookie:
Cookie ck = new Cookie("user", "John");
response.addCookie(ck);Deleting Cookie:
Cookie ck = new Cookie("user", "");
ck.setMaxAge(0);
response.addCookie(ck);Get Cookie:
Cookie ck[] = request.getCookies()HTTPSession
HttpSession interface provides a way to identify the user across multiple requests. Web container creates a session id to identify the particular user. The servlet container uses this interface to create a session between HTTP client and an HTTP server Get HttpSession Object:
public HttpSessiongetSession()Destroy Session:
session.invalidate()Set / Get data in Session:
session.setAttribute(name, value);
session.getAttribute(name);Connecting to JDBC
Java Database Connectivity is commonly used to establish a connection to a database and execute SQL queries.
- Install JAVA and JDBC
- Install a driver on your machine
- Install your DBMS if needed
- Import Packages (java.sql.*)
- Establish Connection
Unit-4
JSP
JSP stands for Java Server Pages. It is a server side technology which is use for creating web applications. It’s used to create dynamic web content. It contains both HTML tags and JSP tags. In JSP tags are used to insert JAVA code into HTML pages. JSP is first converted into servlet by a JSP container before processing the clients request.
Advantages:
- Easy to maintain
- No recompilation or redevelopment
- Less Coding
- Extended version of servlet
Anatomy of JSP
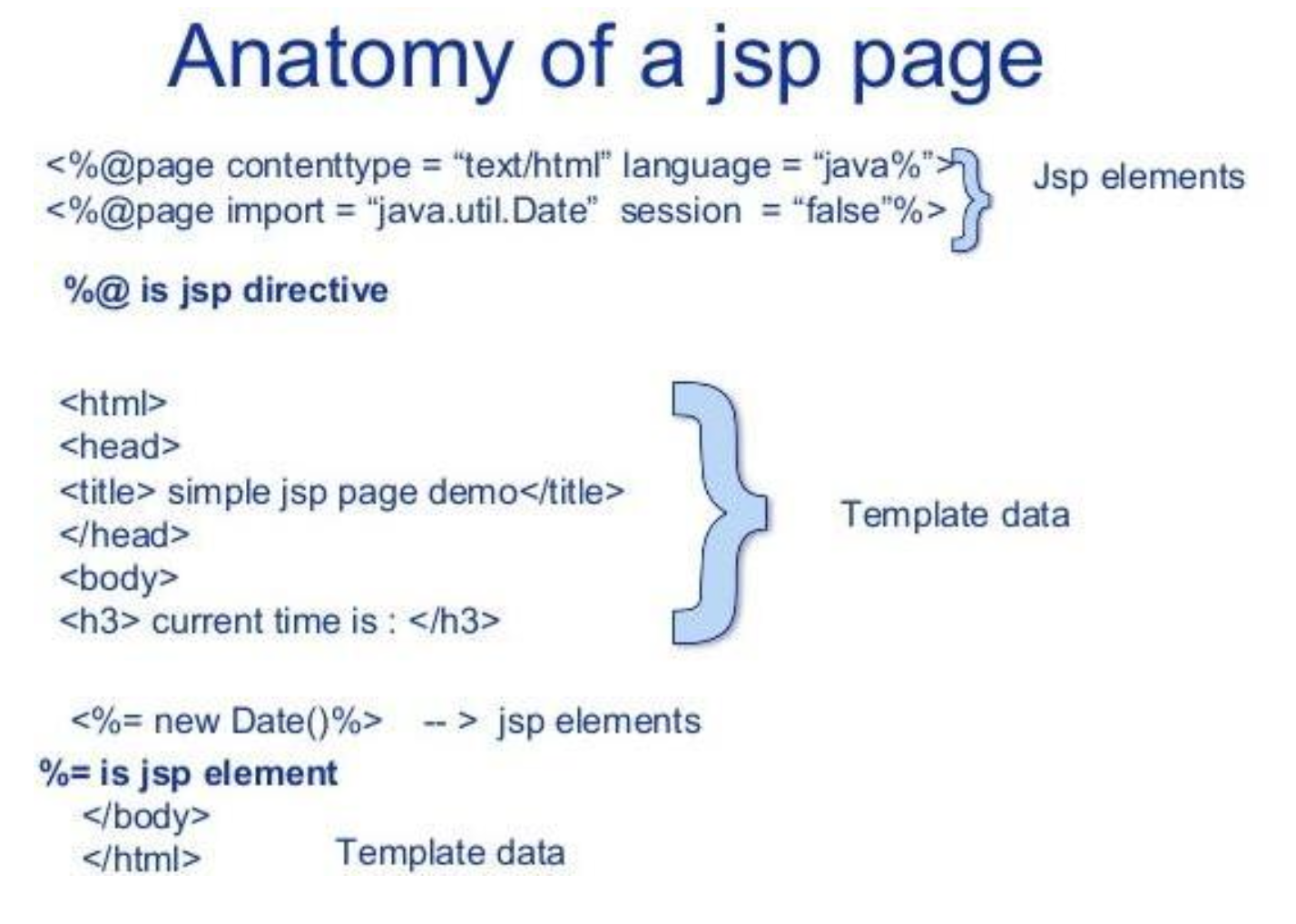
JSP Processing
Once you have JSP capable Web browser, you need to know following things:
- Where to place the files
- How to access the files from your browser
Elements of JSP
Types:
- Expression
- Scriplets
- Directives
- Declarations
Expression
These are one line java expressions, which are relatively small.
<html>
<body>Hello! The time is <%= new java.util.Date() %></body>
</html>Scriplets / Code Snippets
These are multi line java code, used for large blocks of code.
<html>
<body>
<% // Java Code goes here
// It could be multiple lines
%>
</body>
</html>Variables in Scriplets:
- Request
- Response
- Session
- Out
Directives
We can import packages in directives, it starts with <%@.
Syntax:
<%@ directive attribute="value" %>Types:
- page
- include
- taglib
page: Used to provide information about page
<%@ page language="java" %>include: Used include a file in the JSP page
<%@ include file="/header.jsp" %>taglib: Used to use custom tags in JSP pages
<%@ uri="tlds/taglib.tld" prefix="mytag" %>Declarations
Used for defining functions and variables to be used in the JSP
Syntax;
<%!
//java code
%>Example:
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<html>
<body>
<%!
Date theDate = new Date(); Date getDate() {
System.out.println( "In getDate() method" );
return theDate;
}
%>
Hello! The time is now <%= getDate() %>
</body>
</html>JSP Implicit Objects
There are 9 JSP implicit objects. These objects are created by the web container that are available to all JSP pages.
Implicit objects:
- out
- request
- response
- config
- application
- session
- pagecontext
- page
- exception
Session Tracking
Cookies
It’s a small piece of information created by JSP that is stored in client’s machine. They are used to store various kind of information like username and password.
Creating a Cookie:
<%!
Cookie c = new Cookie("empID", "E220");
response.addCookie(c);
%>Reading Cookie:
<%!
Cookie c[] = request.getCookie();
for (i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
String name = c[i].getName();
String value = c[i].getValue();
out.println("name: " + name + " value: " + value);
}
%>Unit-5
PHP
PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor. It’s a server side scripting language that is embedded in html. PHP scripts are executed on the server. It is used to manage dynamic content, databases and session tracking. It supports many databases like MySQL and oracle.
Uses:
- Performs system functions like creating, reading, writing to files
- Modify data in databases
- Access cookie variables and sessions
- Encrypt Data
Characteristics:
- Simplicity
- Efficient
- Security
- Flexibility
- Familiarity
Declaring Variables
All variables are denoted with leading character $. PHP is loosely typed, we don’t have to declare the data type of a variable
Example:
<?php
$str = "John"; // String
$num = 10; // Number
$is_tall = False; // Boolean
?>Data Types
- Integers
- Double
- Boolean
- String
- Arrays
- Objects
Example:
<?php
$str1 = "John"; //String
$str2 = "Doe"
$num1 = 10; //Integer
$num2 = 7.7; //Double
$is_short = True; //Boolean
$arr = array("Apple", "Banana", "Grapes"); //Array
print_r($arr); //Printing array in readable format
$cat = $str1 . $str2; //String Cancatenation
?>Operators
- Arithmetic
- Assignment
- Increment / Decrement
- Comparison
- Conditional
- Logical
Control Structures
- if-else
- else-if
- switch
- while loop
- for loop
- do-while
if-else:
<?php
$num = 10;
if ($num > 5)
echo "Hello World!";
else
echo "This is the way";
?>else-if:
<?php
$num = 10;
if ($num > 15)
echo "Hello World!";
elseif ($num > 10)
echo "This is the way";
else
echo "Foo Bar";
?>Switch:
<?php
$num = 10;
switch($num) {
case 2:
echo "Apple";
break;
case 4:
echo "Banana";
break;
case 6:
echo "Grape";
break;
case 10:
echo "Avacado";
break;
case default:
echo "Orange";
}
?>While Loop
<?php
$num = 1;
while($num < 10) {
echo $num;
$num += 1;
}
?>For Loop
<?php
for($i=0; $i < 6; $i+=1) {
echo $i
}
?>do-while:
<?php
$num = 1
do {
echo $num;
$num += 2;
}while($num < 10);
?>Functions
- Creating Function
- Calling Function
<?php
// Creating function
function hello() {
echo "Hello World!";
}
// Calling function
hello();
?>Functions with parameters:
<?php
function even($num) {
if ($num % 2 == 0)
echo "Even";
else
echo "Odd";
}
even(7);
?>Session Tracking
Cookies
Syntax:
setcookie(name, value, expire)Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<?php
// Setting Cookie
setcookie("Auction_Item", "Luxury Car", time() + 2 * 24 * 60 * 60);
?>
<html>
<body>
<?php
if (isset($_COOKIE["Auction_Item"]))
{
// Accessing Cookie
echo "Auction Item is a " . $_COOKIE["Auction_Item"];
}
else
{
echo "No items for auction.";
}
// Deleting Cookie
setcookie("Auction_Item","", time() - 60);
echo "Cookie is deleted";
?>
</body>
</html>Session
Example:
<?php
// Storing session
session_start();
$_SESSION["Rollnumber"] = "11";
$_SESSION["Name"] = "Ajay";
// Accessing Session
echo 'The Name of the student is :' . $_SESSION["Name"] . '<br>';
echo 'The Roll number of the student is :' . $_SESSION["Rollnumber"] . '<br>';
// Destroying certain session
if(isset($_SESSION["Name"])){
unset($_SESSION["Rollnumber"]);
}
// Destroying all sessions
session_destroy();
?>Connecting to Database
<?php
$host = 'localhost';
$user = 'your_username';
$password = 'your_password';
$database = 'your_database';
// Create a connection to the database
$mysqli = new mysqli($host, $user, $password, $database);
// Example 1: Select data from a table
$query = "SELECT * FROM your_table";
$result = $mysqli->query($query);
echo $result;
// Example 2: Insert data into a table
$insertQuery = "INSERT INTO your_table (name) VALUES ('John Doe')";
if ($mysqli->query($insertQuery) === TRUE) {
echo "Data inserted successfully!";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $mysqli->error;
}
// Close the connection
$mysqli->close();
?>File Handling
Reading file: fread()
<?php
$filename = "input.txt";
$file = fopen($filename, "r");
$size = filesize($filename);
$data = fread($file, $size);
fclose($file);
?>Writing file: fwrite()
<?php
$filename = "input.txt";
$file = fopen($filename, "w");
$txt = "Hello World!";
fwrite($file, $txt);
fclose($file);
?>Appending:
<?php
$filename = "input.txt";
$file = fopen($filename, "a");
$txt = "Hello World!";
fwrite($file, $txt);
fclose($file);
?>Deleting:
<?php
$filename = "input.txt";
unlink($filename);
?>Listing Directories:
<?php
$directory = '/path/to/your/directory';
// Get the list of files and directories in the specified directory
$contents = scandir($directory);
foreach ($contents as $item) {
echo $item;
}
?>